The Process Is the Content Refers to Art Created by Artists Such as
What is Art?
Interactions between the elements and principles of art help artists to organize sensorially pleasing works of fine art while too giving viewers a framework inside which to analyze and discuss artful ideas.
Learning Objectives
Evaluate the frameworks we can use to analyze and discuss works of art
Cardinal Takeaways
Primal Points
- The interplay betwixt the principles and elements of art provide a language with which to discuss and clarify works of art.
- The principles of art include: movement, unity, harmony, variety, residuum, contrast , proportion and pattern.
- The elements of art include: texture , course , infinite , shape, color, value and line .
- How all-time to define the term fine art is a subject of constant contention.
- Since conceptual art and postmodern theory came into prominence, it has been proven that anything can be termed fine art.
Primal Terms
- Formalism:The study of fine art past analyzing and comparison grade and way—the mode objects are made and their purely visual aspects.
What is Fine art?
Fine art is a highly diverse range of human activities engaged in creating visual, auditory, or performed artifacts— artworks—that limited the author's imaginative or technical skill, and are intended to be appreciated for their beauty or emotional ability.
The oldest documented forms of art are visual arts, which include images or objects in fields like painting, sculpture, printmaking , photography, and other visual media . Architecture is frequently included as 1 of the visual arts; nevertheless, like the decorative arts, it involves the cosmos of objects where the practical considerations of use are essential, in a way that they unremarkably are not in another visual art, like a painting.
Fine art may exist characterized in terms of mimesis (its representation of reality), expression, communication of emotion, or other qualities. Though the definition of what constitutes art is disputed and has inverse over time, full general descriptions center on the idea of imaginative or technical skill stemming from human agency and creation. When it comes to visually identifying a work of art, there is no unmarried ready of values or aesthetic traits. A Baroque painting volition not necessarily share much with a contemporary operation slice, just they are both considered art.
Despite the seemingly indefinable nature of art, in that location accept always existed certain formal guidelines for its aesthetic judgment and assay. Formalism is a concept in fine art theory in which an artwork'due south creative value is determined solely by its grade, or how it is made. Formalism evaluates works on a purely visual level, considering medium and compositional elements as opposed to any reference to realism , context, or content.
Fine art is oftentimes examined through the interaction of the principles and elements of art. The principles of art include movement, unity, harmony, variety, balance, contrast, proportion and pattern. The elements include texture, form, infinite, shape, color, value and line. The various interactions between the elements and principles of fine art help artists to organize sensorially pleasing works of art while also giving viewers a framework inside which to analyze and discuss aesthetic ideas.

Ecce Homo, Caravaggio, 1605: This is an case of a Baroque painting.
What Does Art Do?
A central purpose inherent to most artistic disciplines is the underlying intention to appeal to, and connect with, human emotion.
Learning Objectives
Examine the advice, utilitarian, aesthetic, therapeutic, and intellectual purposes of art
Primal Takeaways
Fundamental Points
- The decorative arts add artful and design values to the objects we utilize every day, such as a glass or a chair.
- Art therapy is a relatively young type of therapy that focuses on the therapeutic benefits of fine art-making, using dissimilar methods and theories.
- Since the introduction of conceptual fine art and postmodern theory, it has been proven that annihilation can, in fact, exist termed art.
- It tin can exist said that the fine arts correspond an exploration of the human condition and the effort at a deeper understanding of life.
Cardinal Terms
- human condition:The characteristics, cardinal events, and situations which compose the essentials of human existence, such equally birth, growth, emotionality, aspiration, disharmonize, and mortality.
- fine arts:Visual art created principally for its aesthetic value.
- aesthetic:Concerned with artistic touch on or appearance.
A fundamental purpose common to nigh art forms is the underlying intention to appeal to, and connect with, human emotion. However, the term is incredibly broad and is broken up into numerous sub-categories that lead to utilitarian , decorative, therapeutic, chatty, and intellectual ends. In its broadest form, art may exist considered an exploration of the human condition, or a production of the human experience.
The decorative arts add aesthetic and design values to everyday objects, such equally a glass or a chair, transforming them from a mere utilitarian object to something aesthetically cute. Entire schools of idea exist based on the concepts of blueprint theory intended for the physical world.
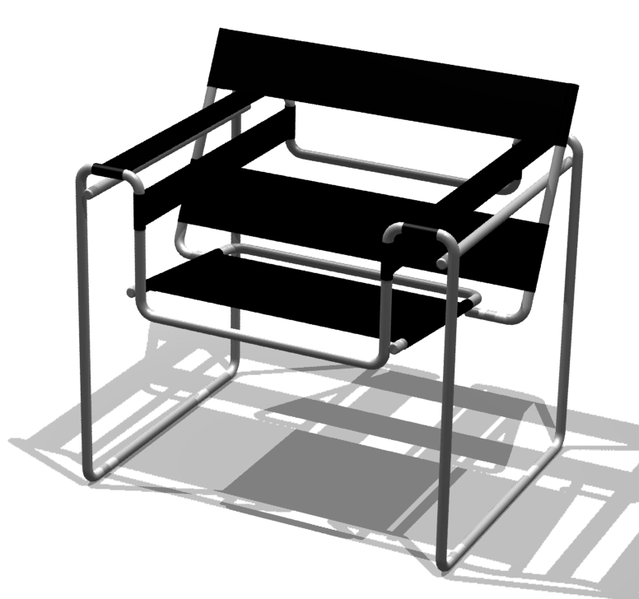
Bauhaus chair by Marcel Breuer: The decorative arts add together artful and blueprint values to everyday objects.
Fine art tin office therapeutically likewise, an thought that is explored in art therapy. While definitions and practices vary, art therapy is generally understood as a class of therapy that uses art media as its main mode of communication. It is a relatively immature discipline, beginning introduced around the mid-20th century.
Historically, the fine arts were meant to entreatment to the homo intellect, though currently in that location are no truthful boundaries. Typically, fine fine art movements have reacted to each other both intellectually and aesthetically throughout the ages. With the introduction of conceptual art and postmodern theory, practically anything can be termed art. In general terms, the fine arts correspond an exploration of the human being condition and the attempt to feel a deeper understanding of life.
What Does Fine art Hateful?
The meaning of fine art is shaped by the intentions of the artist likewise every bit the feelings and ideas it engenders in the viewer.
Learning Objectives
Evaluate the perspectives behind the meaning of art
Key Takeaways
Key Points
- The meaning of fine art is frequently shared among the members of a given order and dependent upon cultural context.
- The nature of art has been described by philosopher Richard Wollheim as "one of the most elusive of the traditional problems of human culture."
- Some purposes of art may be to express or communicate emotions and ideas, to explore and appreciate formal elements for their own sake, or to serve as representation.
- Art, at its simplest, is a class of communication and ways whatever information technology is intended to hateful by the artist.
Cardinal Terms
- mimesis:The representation of aspects of the real world, especially homo actions, in literature and art.
The meaning of art is frequently culturally specific, shared amongst the members of a given society and dependent upon cultural context. The purpose of works of fine art may be to communicate political, spiritual or philosophical ideas, to create a sense of beauty (come across aesthetics), to explore the nature of perception, for pleasure, or to generate stiff emotions. Its purpose may too exist seemingly nonexistent.
The nature of art has been described by philosopher Richard Wollheim as "one of the almost elusive of the traditional problems of human culture." It has been defined equally a vehicle for the expression or communication of emotions and ideas, a means for exploring and appreciating formal elements for their own sake, and equally mimesis or representation. More recently, thinkers influenced by Martin Heidegger take interpreted art as the means by which a community develops for itself a medium for self-expression and interpretation.

Helen Frankenthaler, 1956: A photograph of the American artist Helen Frankenthaler in her studio in 1956.
Fine art, in its broadest sense, is a class of advice. Information technology ways whatever the artist intends it to hateful, and this meaning is shaped by the materials, techniques, and forms it makes utilize of, equally well as the ideas and feelings it creates in its viewers . Art is an deed of expressing feelings, thoughts, and observations.
What Makes Art Beautiful?
Dazzler in terms of art refers to an interaction between line, color, texture, sound, shape, move, and size that is pleasing to the senses.
Learning Objectives
Define "aesthetics" and "beauty" as they relate to art
Key Takeaways
Key Points
- Beauty in art can exist difficult to put into words due to a seeming lack of authentic language.
- An aesthetic judgment cannot be an empirical judgment but must instead be processed on a more intuitive level.
- Aesthetics is the branch of philosophy that deals with the nature and appreciation of art, beauty, and taste. Aesthetics is primal to any exploration of art.
- For Immanuel Kant, the aesthetic experience of dazzler is a judgment of a subjective, simply common, human truth.
- For Arthur Schopenhauer, aesthetic contemplation of beauty is the freest and most pure and true that intellect can be, and is therefore beautiful.
- Art is frequently intended to entreatment to, and connect with, human emotion.
Primal Terms
- aesthetics:The branch of philosophy dealing with the nature of fine art, taste, and the cosmos and appreciation of dazzler.
- intuitive:Spontaneous, without requiring conscious idea; easily understood or grasped by instinct.
What makes art beautiful is a complicated concept, since beauty is subjective and can modify based on context. However, there is a basic human instinct, or internal appreciation, for harmony, remainder, and rhythm which can be defined equally beauty. Beauty in terms of art usually refers to an interaction between line, color, texture , sound, shape, motion, and size that is pleasing to the senses.
Aesthetic Art
Aesthetics is the co-operative of philosophy that deals with the nature and appreciation of art, beauty, and taste. Aesthetics is fundamental to whatever exploration of art. The word "artful" is derived from the Greek "aisthetikos," significant "esthetic, sensitive, or sentient. " In practice, artful judgment refers to the sensory contemplation or appreciation of an object (not necessarily a piece of work of art), while artistic judgment refers to the recognition, appreciation, or criticism of a work of fine art.
Numerous philosophers accept attempted to tackle the concept of beauty and art. For Immanuel Kant, the artful experience of beauty is a judgment of a subjective, merely common, human truth. He argued that all people should agree that a rose is beautiful if information technology indeed is. There are many common conceptions of beauty; for instance, Michelangelo'southward paintings in the Sistine Chapel are widely recognized as cute works of fine art. However, Kant believes beauty cannot be reduced to any basic set of characteristics or features.
For Arthur Schopenhauer, aesthetic contemplation of beauty is the freest and most pure that intellect can be. He believes that only in terms of aesthetics practise we contemplate perfection of form without any kind of worldly calendar.

Michelangelo, The Cosmos of Adam, The Sistine Chapel, 1508-1512:
Beauty in art can be difficult to put into words due to a seeming lack of accurate linguistic communication. An artful judgment cannot exist an empirical judgment but must instead be processed on a more intuitive level.
Art and Homo Emotion
Sometimes beauty is non the creative person's ultimate goal. Art is oftentimes intended to appeal to, and connect with, homo emotion. Artists may express something so that their audience is stimulated in some mode—creating feelings, religious religion, curiosity, interest, identification with a grouping, memories, thoughts, or creativity. For case, functioning art often does non aim to please the audience but instead evokes feelings, reactions, conversations, or questions from the viewer . In these cases, aesthetics may be an irrelevant measure of "cute" art.
Who Is an Artist?
An creative person is a person who is involved in the broad range of activities that are related to creating art.
Learning Objectives
Summarize the evolution of the term "artist" and its predecessors
Fundamental Takeaways
Fundamental Points
- In ancient Hellenic republic and Rome there was no word for "artist," only there were nine muses who oversaw a different field of human creation related to music and poetry, with no muse for visual arts.
- During the Heart Ages , the word "artista" referred to something resembling "craftsman."
- The kickoff segmentation into major and modest arts dates back to the 1400s with the piece of work of Leon Battista Alberti.
- The European Academies of the 16th century formally solidified the gap between the fine and the applied arts which exists in varying degrees to this solar day.
- Currently an artist can be divers as anyone who calls him/herself an creative person.
Key Terms
- muses:Goddesses of the inspiration of literature, science, and the arts in Greek mythology.
- Popular fine art:An art motility that emerged in the 1950s that presented a challenge to traditions of fine art by including imagery from popular culture such as advert and news.
- fine arts:The purely aesthetic arts, such as music, painting, and poesy, as opposed to industrial or functional arts such as engineering or carpentry.
An artist is a person who is involved in the wide range of activities that are related to creating fine art. The word has transformed over time and context, but the modern agreement of the term denotes that, ultimately, an artist is anyone who calls him/herself an artist.
In ancient Greece and Rome, there was no discussion for "artist." The Greek word "techne" is the closest that exists to "art" and means "mastery of any fine art or arts and crafts." From the Latin "tecnicus" derives the English language words "technique," "technology," and "technical." From these words nosotros can denote the ancient standard of equating art with manual labor or craft.
Each of the nine muses of ancient Greece oversaw a different field of human creation. The creation of poetry and music was considered to exist divinely inspired and was therefore held in high esteem. All the same, there was no muse identified with the painting and sculpture; aboriginal Greek civilisation held these art forms in depression social regard, because work of this sort to be more than along the lines of manual labor.
During the Middle Ages, the word "artista" referred to something resembling "craftsman," or student of the arts. The get-go sectionalisation into "major" and "pocket-sized" arts dates back to the 1400s with the work of Leon Battista Alberti, which focused on the importance of the intellectual skills of the artist rather than the manual skills of a craftsman. The European academies of the 16th century formally solidified the gap between the fine and the practical arts, which exists in varying degrees to this twenty-four hour period. Generally speaking, the applied arts apply design and aesthetics to objects of everyday use, while the fine arts serve every bit intellectual stimulation.
Currently, the term "artist" typically refers to anyone who is engaged in an activity that is deemed to exist an fine art class. Nonetheless, the questions of what is art and who is an artist are not easily answered. The thought of defining art today is far more difficult than it has always been. Afterwards the exhibition during the Popular Art movement of Andy Warhol's Brillo Box and Campbell's Soup Cans, the questions of "what is art?" and "who is an artist?" entered a more conceptual realm. Anything tin, in fact, be art, and the term remains constantly evolving.

Andy Warhol, Campbell'south Soup Cans, 1962: Andy Warhol'southward Campbell's Soup Cans take come to be representative of the Pop Fine art movement.
Source: https://courses.lumenlearning.com/boundless-arthistory/chapter/what-is-art/
0 Response to "The Process Is the Content Refers to Art Created by Artists Such as"
Post a Comment